Cobalt Uses and Applications
Current uses of cobalt are as follows.
Metallic uses include super alloys for the aerospace industry to make power and jet engine turbines, cutting tools and cemented carbides used to machine steel, and electromechanical devices such as magnets, electric motors, generators, transformers and magnetic storage tape and hard disks.

Chemical uses include sulphates for manufacturing rechargeable batteries, catalysts for petroleum refining and to manufacture plastics, and as pigments.

Clean air uses include oil desulfurization, fuel cells, hybrid vehicles, gas/coal to liquid technologies.

Renewable energy uses include solar power, wind turbines, geothermal power plants, gas turbines, conversion of biomass to hydrogen and hydrogen storage.

Health uses include it as a key component of Vitamin B12 which is essential for human health and necessary for neurological function, brain function and the formation of blood. Cobalt is also used in prosthetics, cancer treatments and food preservation.

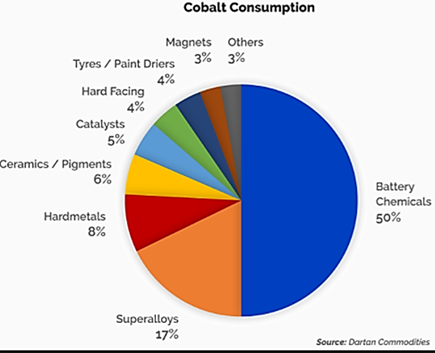
Battery uses Cobalt is critical for manufacturing high performance rechargeable batteries that are used in portable electronics, electric vehicles and stationary power storage applications. In the mid 1990’s, only 1% of cobalt demand was from its use in rechargeable batteries for electronics. However, the growing importance of lithium-ion and nickel metal hydride batteries in smartphones and other electronic devices contributed to the demand for cobalt in rechargeable batteries surpassing its use in super alloys sector for the first time in 2007. Rechargeable batteries have since been the largest end use of cobalt, accounting for 50% of cobalt demand in 2016.
The transformative evolution to electric vehicles and the need for stationary storage of power from renewable sources is anticipated to further boost the demand for cobalt in batteries.